What is Supervised Learning in AI? And How Does It Work?


Have you ever questioned yourself about how AI systems can make a decision that you can actually trust, such as warning about a fraudulent transaction or accurately forecasting customer demand? Topics that many businesses find difficult with AI models that seem like black boxes deliver results that are not clear and consistent.
Such uncertainty usually gives rise to poor adoption, wasted data efforts, and lost opportunities. Here, Supervised Learning in AI comes in. Supervised learning will allow AI systems to learn correctly, act predictably, and provide quantifiable outputs by training models with labeled data and well-defined results.
You will get to know the nature of supervised learning in AI, the key concept of supervised learning, its functioning in detail, the difference between supervised and unsupervised learning, and the areas where supervised learning models add real value in real business-driven systems.
Supervised Learning in AI is a machine learning model that uses labels in training. Every input has a known, correct output, and the system is able to learn a clear relationship between the two. This is with the aim of enabling the AI to make correct predictions or decisions when it comes across new data in the real world.
A machine learning supervised model is figured by repeated comparison of its predictions against the true results and modification of the model to minimize the errors. It is this feedback loop that renders supervised learning very reliable and performance-based.
The advantage of supervised learning:
Supervised learning in AI is clearly result-oriented, unlike non-supervised learning, where patterns are found independently. It is why supervised learning models are particularly appropriate to the problems of classification and regression, where accuracy, control, and consistency are essential to production-friendly AI systems.
Practical examples of supervised learning in AI can be learned more easily. These are examples of how labeled data is converted into correct, real-life predictions.
Let’s take the case of an email spam filter. The model is trained using a collection of thousands of spam or non-spam emails. The supervised learning model is able to classify new incoming emails correctly by learning patterns like keywords, sender behavior, and formatting. It is a typical supervised learning example where the results are well specified and quantifiable.
Supervised machine learning examples in the real world
AI supervised learning entails a structured feedback-based process, which assists models to learn correct input-output relationships. All the stages are important in making sure that the model is reliable in the real world.
It starts by collecting data and labeling the appropriate inputs. These labels determine what the model ought to have learned, and hence, data quality and accuracy are essential to supervised learning.
The labeled data is fed into a supervised algorithm, where the model identifies patterns and relationships. During training, the model continuously adjusts its parameters to minimize prediction errors.
After training, the model is tested on the unseen data to test the performance of the model. Accuracy and error rate are metrics that can be used to assess the degree of a supervised learning model’s generalization outside the training data.
Once validated, the model is deployed to give predictions on actual data. This is where AI supervised learning provides concrete value to realize historical data into actionable information with predictable and consistent results.
Supervised learning in AI is divided according to the nature of the output that the model is being trained to predict. When making the correct type selection is necessary to create business and accurate AI solutions.

Used when the output is a fixed category or label. The model learns from labeled examples and assigns new data points to one of the predefined classes. This approach is common in problems where decisions must be discrete and clearly defined.
Used in the case when the output is a continuous numerical value. The model does not make predictions of a class; instead, it estimates a real-world quantity using known patterns in the labeled data.
The two are the foundations of supervised learning models, which allow machine learning supervised systems to provide accurate and results-oriented predictions in diverse AI application development services.
In AI, supervised learning uses clearly defined algorithms to extract patterns of known cases and apply them to their predictions. All the supervised learning algorithms are adapted to particular problems, data amount, and performance demands.
Applied to the prediction of continuous values by modeling the association among the input variables and a numerical output. Usually, in forecasting and trend analysis.
This is a classification-oriented supervised learning algorithm, despite its name. It estimates the likelihood of an occurrence falling within a particular category, which is appropriate in binary decision-making.
A rule-based supervised algorithm that splits data into branches based on feature values. Decision trees can be easily interpreted and are used in business decision systems.
A collection of several decision trees that enhances accuracy and reduces overfitting. It is a supervised machine learning algorithm that works well on high-dimensional and complex datasets.
SVMs are applied to both classify and regress data, and they determine the best boundary that defines data points. They work well when there are definite gaps between classes.
An uncomplicated supervised learning algorithm that uses the similarity of data to the local labeled examples to classify the data. Most appropriate for smaller datasets.
State-of-the-art supervised learning models that can learn more nonlinear relationships. They are usually applied in image recognition, speech processing, and deep learning.
Together, these supervised learning algorithms form the core of machine learning supervised systems, enabling AI solutions to deliver reliable, measurable, and production-ready results.
Supervised learning in AI, where labeled data is used, whereby each input is matched with a known output. This enables models to acquire explicit relationships and give accurate and quantifiable predictions, and this makes supervised learning best suited for business-critical applications.
Unsupervised or non-supervised learning, on the other hand, processes unlabeled data and does not generate foregone conclusions but finds out concealed patterns in the data.
In the comparison of supervised vs unsupervised learning, control and exploration are the main differences between them. Supervised learning models are used where accuracy and reliability is require,d whereas unsupervised learning is best applied in the analysis of data and identification of trends.
| Aspect | Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
| Data type | Use labeled data | Use unlabeled data |
| Learning approach | Learn from known outputs | Discover patterns independently |
| Output | Predictable and measurable | Exploratory and pattern-based |
| Accuracy control | High and trackable | Limited and interpretive |
| Common use cases | Classification, regression, forecasting | Clustering, segmentation, anomaly detection |
| Business Suitability | Ideal for production-ready AI | Best for insights and data exploration |
While supervised vs unsupervised learning serve different purposes, supervised learning models are preferred when businesses need reliable predictions and clearly measurable results.
Supervised Learning in AI has been among the best and most reliable methods of creating intelligent systems that provide accurate, explainable, and measurable results. Through the study of labeled data, supervised learning models might be able to solve problems that are defined well and provide confidence in their solution, be it classification, prediction, or forecasting.
From basic supervised learning instances, such as spam detection, to sophisticated supervised machine learning instances in healthcare, finance, and enterprise automation, this methodology still drives real-world AI success.
Comparison of supervised vs unsupervised Supervised learning is more advantageous due to control and reliability, whereas unsupervised learning is effective in discovery-based understanding. Considering such a variety of supervised learning algorithms and supervised machine learning algorithms, selecting an appropriate supervised algorithm is determined by the quality of data, the nature of the problem, and the objectives of the business. Regardless of hiring a freelance AI developer or engaging a trusted AI development company, supervised learning in AI is the foundation of scalable solutions deployed by contemporary AI application development firms through the services of competent AI application developers.
Get clarity on use cases, architecture, costs, and timelines with insights from 50+ real-world AI implementations.
The concept of Supervised Learning in AI is a machine learning method that involves training the model using labeled data, i.e., every input has an established output. That assists the system in acquiring the correct input-output relationships and provides valid predictions on new data.
Data labelling is the key distinction between supervised and unsupervised learning. In supervised learning, accuracy and control are achieved by using labeled data, and in non-supervised learning, patterns are found using unlabeled data and no predetermined results.
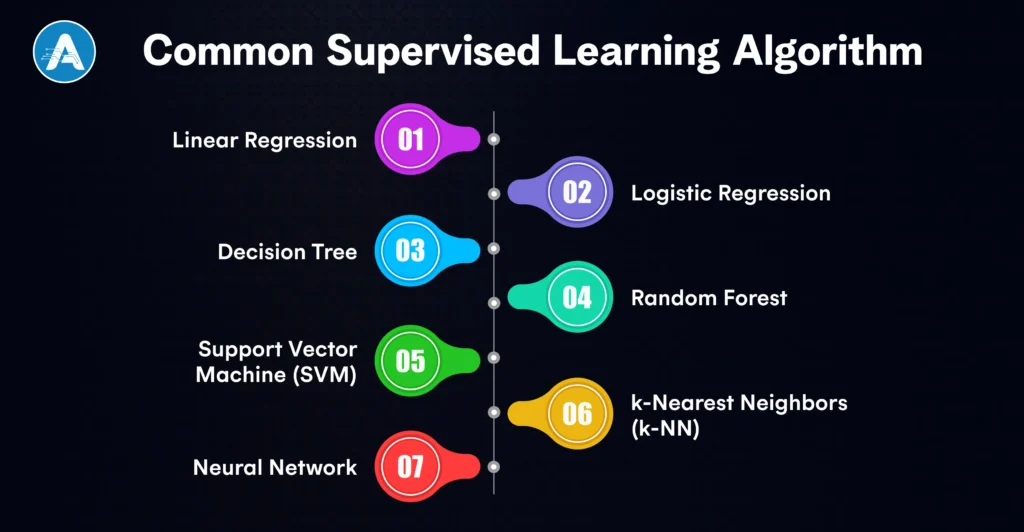
Some of the most popular supervised learning algorithms are Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, Decision Trees, Random Forest, Support Vector Machines, k-NN, and Neural Networks. These monitored algorithms find extensive applications in AI systems of the real world.
An example of a classical supervised learning is spam detection in emails, whereby emails are tagged as spam or not spam. The model is made to learn these labels in order to appropriately classify new emails.
Supervised learning models should be applied by businesses in situations when they possess labeled historical data and require precise, quantifiable predictions to complete tasks such as forecasting, classification, or risk analysis.
In cases of complexity of projects, firms might have a freelance AI programmer or retain an AI development firm that provides end-to-end services to develop AI applications, which are headed by seasoned AI application developers.
Continue exploring AI and technology insights

Design workflows are evolving at breakneck speed. AI Image Generators have officially transitioned from experimental “toys” to essential everyday assets for modern creatives. The…

Many AI apps for iPhone are very good, but it’s more difficult to decide which ones are worth keeping. With hundreds of AI apps…

Websites don’t start with layouts; they start with purpose. A free AI website builder can now launch over 90% of first-time websites in under…