Vector Database vs Graph Database: A Guide to Choosing the Right Solution

In the race for AI dominance, your database is the brain of your application. For years, businesses relied on traditional rows and columns to organize their world. But as we move into the era of Generative AI and hyper-connected networks, those old structures are now on the verge of collapse.
When comparing a Vector Database vs Graph Database is no longer just about storage; it is about how your business retrieves meaning and identifies hidden patterns.
These two technologies have emerged as the primary contenders for modern data architecture, determining how fast your AI “thinks,” how accurately you detect fraud, and how effectively you understand complex customer needs.
This is why many organizations validate their data architecture with an experienced AI development company before committing to a long-term AI foundation.
Choosing the wrong foundation can lead to high latency, AI hallucinations, and missed insights. Picking the right one or a strategic combination of both can be the competitive advantage that scales your business.
In this guide, we’ll break down the Vector Database vs Graph Database debate, explore real-world graph database examples, and help you decide which architecture will drive the most impact.
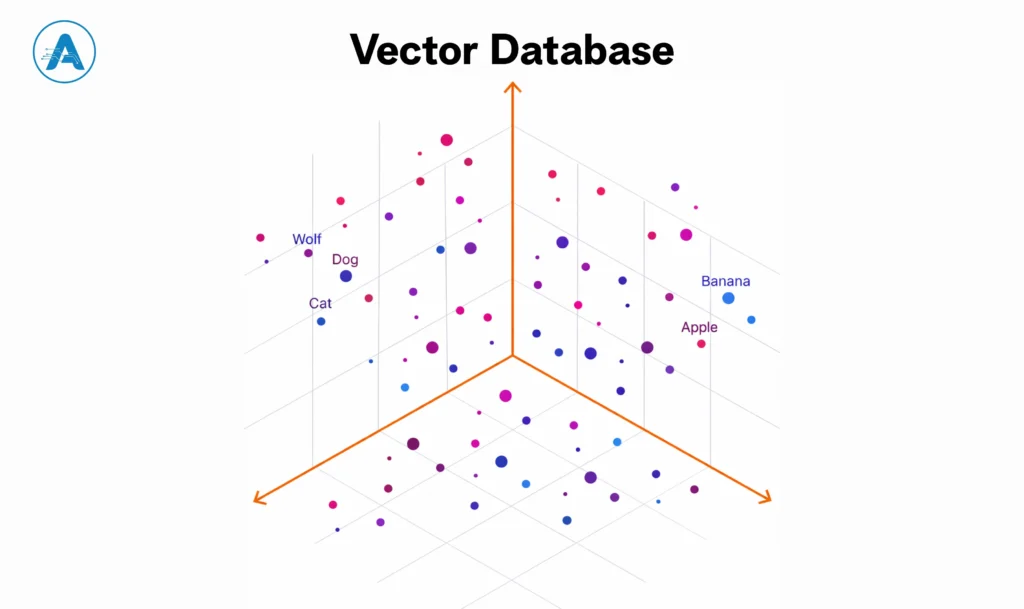
A vector database is constructed to know the context and not merely to match the keywords. It does not use rows and columns to store information, but as embeddings, mathematical coordinates that define the content of a piece of information.
Did you ever ask yourself who Vector is? Technically speaking, a numerical representation is used to make a computer know how various ideas interact with each other within a digital space. Unstructured data such as PDFs, images, and audi,o is processed by the real power of an AI vector approach.
For an AI application developer, a vector database makes it possible to build intelligent features like semantic search and recommendations without relying on rigid keyword logic.
When you are building in vector environments, you unlock Semantic Search. This implies that by simply typing in a query such as a reliable family car, the database will not go and find the exact words; it will find out the intent and give results of minivans or the highest-rated SUVs. By focusing on meaning rather than spelling, you provide a smarter, more human-like experience for your users.
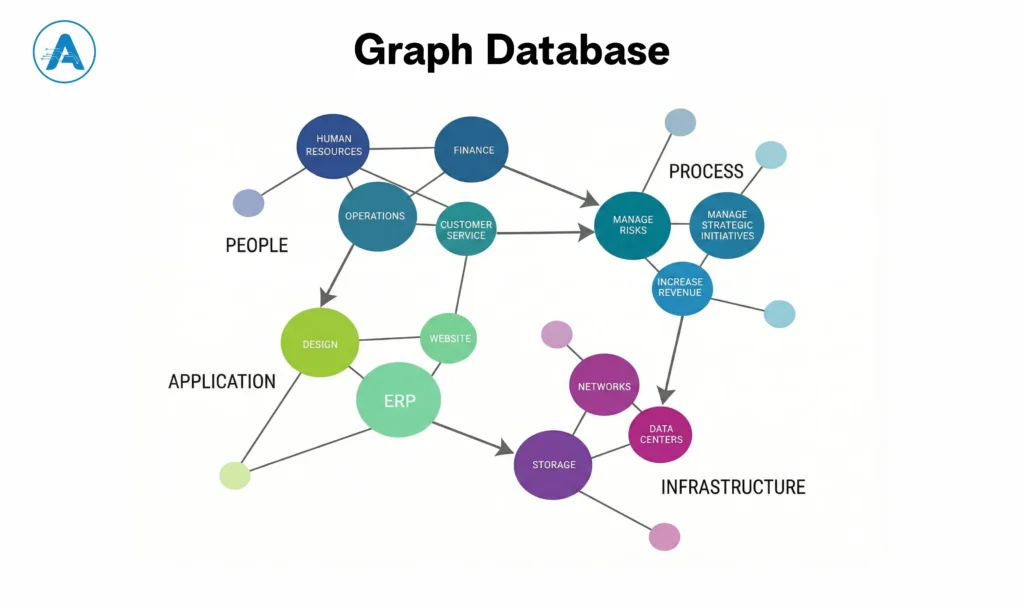
While vectors are concerned with vibes, a graph database is concerned with relationships. It does not seek similarities with things; rather, it traces the connection between various pieces of information. Data points in this system are nodes, and the relationship between the nodes is the edges. This network is incredibly easy to bridge the dots of huge networks.
Consider some graph DB examples you use every day:
The approach of having an example graph database enables the business to respond to intricate queries that are not possible in a traditional database. An example is that, rather than simply inquiring what this customer purchased, the graph database can respond, “Who else purchased this item, and what did the other users purchase that this user has not yet viewed? When you focus on the connection between the data points, you can have a profound, structural insight into your whole business ecosystem.
Choosing the right tool depends on the “question” you are trying to answer. Use this guide to determine which architecture will drive the most impact for your project.
| Feature | Vector Database | Graph Database |
| Core Purpose | Finds similarity and meaning | Finds relationships and connections |
| Data Representation | Numerical vectors (embeddings) | Nodes (entities) and edges (relationships) |
| Best At | Semantic search, recommendations, and AI chat | Network analysis, fraud detection, knowledge graphs |
| Query Style | Find items similar to this | How are these items connected? |
| AI Usage | Very high | Moderate |
| Handles Context | Yes, understands intent and meaning | Limited, focuses on structure |
| Typical Queries | Similarity search, nearest neighbor | Multi-hop path traversal |
| Performance Focus | Fast similarity matching | Fast relationship traversal |
| Common Use Cases | AI chatbots, RAG, and personalization | Social networks, fraud systems, supply chains |
| Scalability Model | Optimized for high-dimensional data | Optimized for growing relationship graphs |
| Business Impact | Better relevance, smarter AI results | Better visibility into complex connections |
Choosing between these two isn’t about which technology is better; it’s about which one solves your specific business bottleneck. Industry leaders across finance, healthcare, and retail are already using these tools to redefine their operations.
Use the following framework to determine which solution aligns with your technical and business requirements.
You are focused on human-like interaction and content discovery. This is the primary choice for businesses building modern AI applications that handle fuzzy or unstructured data.
1. Retail/Media: Companies like Spotify and Amazon use vector similarity to power recommendation engines. They do not simply match a genre but, instead, with the help of an AI vector, identify songs and products that feel the same according to thousands of hidden features.
2. Healthcare: Pharmaceutical companies such as GSK discover drugs with the help of the vector databases. They can instantly recognize similar molecule structures, which may cure the same disease, since chemical compounds are represented as vectors.
3. Best for:
You are concerned about complex tracing, safety, and network integrity. This architecture is necessary when the connection between two things is more desirable than the things themselves.
1. Finance: Major banks and sites such as PayPal use graph DB examples to prevent scam rings. A vector database may identify a transaction that looks suspicious, but a graph database will trace the money through ten different accounts to identify the hidden individual who is pulling the strings.
2. Logistics: Supply chain managers construct a digital twin of their network by using graph databases. When one port in Asia is shut down, the graph immediately finds all the missed shipments as well as all the impacted customers in all parts of the world.
3. Best for:
While the debate of Vector Database vs Graph Database often frames them as competitors, the most sophisticated AI systems in 2026 are actually using both. This is known as a vector grapher approach or GraphRAG, which merges the intuitive feel of an AI vector with the rigid logic of a graph database.
Implementing a hybrid vector and graph approach is where experienced AI application development services add the most value, balancing accuracy, performance, and scalability.
A hybrid model is more complex than using a standalone vector database or graph database, but for certain businesses, it is the most reliable and future-ready choice. You should consider this approach if accuracy, reasoning, and context are critical to your product or decision-making.

In business sectors like finance, legal, and healthcare industries, it is not sufficient to be approximately right. Responses should be demonstrably right.
In this case, organizations tend to apply:
As an example, an AI system can find pertinent medical research by means of a vector search and then cross-verify the official clinical databases by cross-reference by graph relationship to guarantee accuracy. This type of hybrid configuration greatly minimizes fake news and AI delusions.
Similarity is the strength of vector databases, whereas multi-step reasoning is their weakness. Graph logic is required with relationship-heavy questions.
Consider a query like: “Give me a luxury hotel in Paris where my business associate was staying last year.” This is solved by a hybrid system:
This combination provides the accurate answers that could not have been given by each of the systems separately.
Context-only is not sufficient in a place where data keeps changing, like in a stock market or supply chain across the globe, or real-time risk systems.
A hybrid system enables systems to:
This allows quicker actions, improved forecasting, and enhanced decision-making in situations that are fast-changing.
Choosing between a Vector Database vs Graph Database comes down to how your business thinks and decides. Vector databases help AI understand meaning and intent, while graph databases reveal how data points connect and influence each other. Each solves a different problem, and both are essential in modern AI architecture.
The most successful systems are built with clarity, not trends. Whether you choose a vector database, a graph database, or a hybrid of both, the right foundation will reduce latency, improve accuracy, and unlock insights that drive real business impact.
In the AI era, your database is no longer just infrastructure; it’s the intelligence behind every decision you make.
Get clarity on use cases, architecture, costs, and timelines with insights from 50+ real-world AI implementations.
A graph database is best when relationships are critical. This includes fraud detection, social networks, supply chains, identity management, and knowledge graphs, anywhere connections matter more than similarity.
No. In the Vector Database vs Graph Database comparison, neither replaces the other. They solve fundamentally different problems. Vector databases understand meaning; graph databases understand structure and relationships.
Yes. Many modern AI systems use a hybrid approach, combining vector databases for semantic understanding and graph databases for logical reasoning. This approach is often called GraphRAG or a vector grapher strategy.
For most AI-driven applications, vector databases are essential because they work directly with embeddings and AI vectors. However, AI systems that require traceability, explainability, or multi-step reasoning benefit greatly from graph databases.
Traditional SQL databases struggle with both. They are not optimized for high-dimensional vector search or multi-hop relationship queries, which is why specialized solutions are preferred in Vector Database vs Graph Database scenarios.
Yes. Choosing the right architecture or a hybrid can significantly reduce AI hallucinations by grounding responses in relevant context (vector) and verified relationships (graph).
Continue exploring AI and technology insights

Design workflows are evolving at breakneck speed. AI Image Generators have officially transitioned from experimental “toys” to essential everyday assets for modern creatives. The…

Have you ever questioned yourself about how AI systems can make a decision that you can actually trust, such as warning about a fraudulent…

Many AI apps for iPhone are very good, but it’s more difficult to decide which ones are worth keeping. With hundreds of AI apps…